Cost of Steel Siding vs Vinyl A Homeowners Guide

Cost of steel siding vs vinyl: Choosing the right siding for your home is a big decision, impacting both your wallet and your home’s curb appeal. This guide breaks down the costs, from initial investment to long-term maintenance, helping you make an informed choice. We’ll explore everything from material and labor costs to energy efficiency and environmental impact, so you can weigh the pros and cons of each option.
Understanding the differences between steel and vinyl siding goes beyond just the price tag. Factors like durability, maintenance requirements, and aesthetic preferences play a significant role. This comparison will illuminate the total cost of ownership over time, allowing you to confidently select the siding that best fits your needs and budget. We’ll delve into the specifics of each material, providing clear and concise information to help you navigate this important home improvement decision.
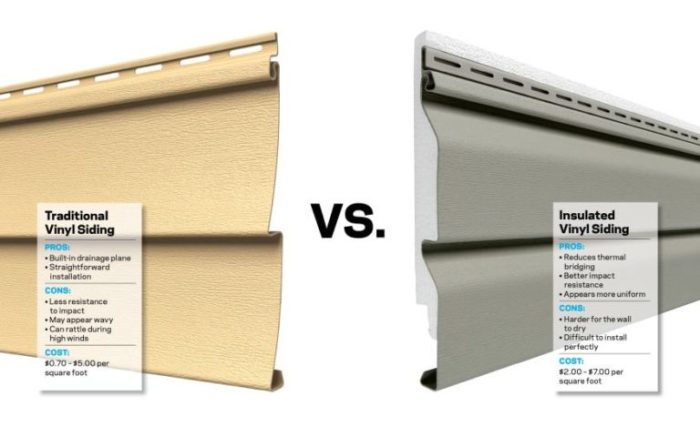
Initial Costs

Source: sidingauthority.com
Choosing between steel and vinyl siding involves a significant upfront investment. Understanding the cost breakdown for materials and labor is crucial for making an informed decision. This section will detail the estimated costs for a 1500 sq ft house, acknowledging that prices can vary based on location, supplier, and project specifics.
Material Costs: Steel vs. Vinyl Siding
Estimating material costs requires considering several factors. For a 1500 sq ft house, we’ll assume an average siding coverage area, accounting for overlaps and waste. Steel siding typically costs more upfront than vinyl, primarily due to the higher cost of raw materials and manufacturing processes. Delivery fees will also vary based on distance and supplier. Waste generation is generally lower with steel siding as it’s less prone to damage during installation compared to vinyl. However, both materials require some allowance for cuts and mishaps.
Let’s assume the following (these are estimates and can vary greatly based on location and specific product choices):
Steel Siding:
* Materials: $10,000 – $15,000 (This range accounts for variations in gauge, color, and style)
* Delivery: $500 – $1000
* Waste Allowance: 5-10% of material cost ($500 – $1500)
Vinyl Siding:
* Materials: $6,000 – $10,000 (This range reflects different quality levels and styles)
* Delivery: $300 – $700
* Waste Allowance: 10-15% of material cost ($600 – $1500)
Labor Costs: Steel vs. Vinyl Siding Installation
Labor costs represent a significant portion of the overall project expense. The complexity of installation differs between steel and vinyl siding. Steel siding, being heavier and requiring more specialized tools and expertise, generally commands higher labor rates. Geographic location plays a crucial role; labor rates in high-cost areas will be considerably higher. The experience level of the installer also impacts the final cost; experienced installers may charge more but often complete the job faster and more efficiently, potentially offsetting some of the higher hourly rate.
For a 1500 sq ft house, we can estimate labor costs as follows:
Steel Siding:
* Labor: $8,000 – $15,000 (This broad range accounts for regional variations and installer experience)
Vinyl Siding:
* Labor: $5,000 – $10,000 (This range reflects differences in installer experience and location)
Total Initial Costs Comparison
The table below summarizes the estimated total initial costs for both steel and vinyl siding for a 1500 sq ft house. Remember that these are estimates, and actual costs may vary significantly depending on several factors.
| Material | Labor | Total Cost | Siding Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| $10,000 – $16,500 | $8,000 – $15,000 | $18,000 – $31,500 | Steel |
| $6,000 – $11,500 | $5,000 – $10,000 | $11,000 – $21,500 | Vinyl |
Long-Term Costs
Source: aicroofing.com
Choosing between steel and vinyl siding involves considering not only the upfront costs but also the long-term expenses associated with maintenance and repairs. Both materials have different lifespans and require varying levels of upkeep, significantly impacting your overall investment over time. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your budget and long-term goals.
Over 20 years, the maintenance and repair needs of steel and vinyl siding diverge considerably. While both require occasional cleaning, the frequency and type of maintenance differ significantly, as do the potential repair costs associated with damage.
Maintenance Needs for Steel and Vinyl Siding
Steel siding generally requires less maintenance than vinyl. Regular cleaning, perhaps once or twice a year using a garden hose and mild detergent, is usually sufficient to remove dirt and debris. However, steel can be prone to rusting, especially in coastal areas or if the protective coating is damaged. This may require spot repairs or repainting every 10-15 years, depending on the quality of the initial coating and environmental factors. Vinyl siding, on the other hand, is typically low-maintenance. It’s resistant to rust and rot, and cleaning usually involves occasional washing with soap and water. However, it can become brittle and fade over time, particularly with prolonged sun exposure.
Repair Costs Associated with Siding Damage
Both steel and vinyl siding are susceptible to damage from impacts (e.g., falling branches, sports equipment) and severe weather events (e.g., hail, high winds). Repair costs vary significantly depending on the extent of the damage. For steel siding, a small dent might only require a simple repair using a filler and paint, costing perhaps $50-$100. More extensive damage, such as a large hole or significant rust, may necessitate panel replacement, potentially costing several hundred dollars per panel, depending on the size and the need for professional installation. Vinyl siding repairs are generally less expensive. Replacing a damaged vinyl panel is relatively straightforward and inexpensive, often costing between $20 and $50 per panel, including the cost of the replacement panel and labor. However, extensive storm damage could necessitate replacing multiple panels, increasing the overall repair cost. For instance, hail damage might require replacing several panels, leading to a total repair cost in the range of $200-$500 depending on the extent of the damage.
Lifecycle Cost Comparison (20 Years), Cost of steel siding vs vinyl
Comparing the lifecycle costs of steel and vinyl siding requires considering initial costs, maintenance, and repairs over 20 years. It’s difficult to provide exact figures, as costs vary based on factors like location, labor costs, and the quality of the materials. However, a general comparison can illustrate the potential differences.
- Steel Siding: Higher initial cost, lower maintenance costs (excluding potential repainting), moderate repair costs (potentially high for extensive damage).
- Vinyl Siding: Lower initial cost, very low maintenance costs, lower repair costs (unless extensive damage occurs).
For example, let’s assume an initial cost of $10,000 for steel and $7,000 for vinyl siding on a typical house. Over 20 years, steel might require repainting for $2,000 and occasional minor repairs totaling $500. Vinyl might require minor repairs costing around $300 over the same period. This illustrates that while vinyl has a lower initial cost, the overall cost difference over 20 years might be less significant than initially anticipated, particularly if steel requires only minimal repairs. The actual costs will vary greatly depending on location, the severity of weather events, and the quality of the installation and materials used.
Energy Efficiency and Savings

Source: homeprofy.com
Choosing between steel and vinyl siding involves considering more than just initial costs; long-term energy efficiency plays a significant role in your overall savings. Both materials offer different levels of insulation, impacting your heating and cooling bills. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and environmental goals.
Steel and vinyl siding differ significantly in their thermal properties. Steel, while a good conductor of heat, can be engineered for better energy efficiency through the use of insulation backing. Vinyl, on the other hand, is a relatively poor conductor, offering inherent insulation benefits. However, the quality and thickness of vinyl siding can greatly influence its insulating capabilities. This section will delve into the specific energy efficiency characteristics of each material and their impact on your energy costs.
Steel Siding’s Energy Efficiency
Steel siding, when properly installed with appropriate insulation, can significantly improve a home’s energy efficiency. The insulating layer behind the steel acts as a barrier against heat transfer, reducing the amount of energy needed to heat or cool the house. For example, a home in a cold climate fitted with steel siding and a robust insulation system might see a reduction in heating costs by 15-20% compared to a home with less efficient siding. This reduction comes from minimizing heat loss through the walls. The effectiveness of steel siding’s insulation heavily depends on the type and thickness of the insulation used, as well as the quality of installation. Poor installation can negate much of the intended energy savings.
Vinyl Siding’s Energy Efficiency
Vinyl siding offers inherent insulation properties due to its lower thermal conductivity compared to steel. However, the degree of energy savings depends on the thickness and quality of the vinyl. Thicker vinyl siding generally provides better insulation. A home in a hot climate with high-quality, thick vinyl siding may experience a reduction in cooling costs of around 5-10%, primarily due to reduced heat absorption. Unlike steel, vinyl siding’s insulation is inherent to the material itself, and doesn’t rely on added insulation layers. Nevertheless, proper installation remains crucial to maintain its energy-saving potential.
Comparative Energy Savings Over 10 Years
The following table demonstrates the potential energy savings (or costs) associated with each siding type over 10 years, considering varying climate conditions. These figures are estimates and can vary based on factors such as home size, insulation quality, energy prices, and individual heating/cooling habits. The data is based on average energy consumption patterns and cost fluctuations in different climate zones.
| Climate Zone | Steel Savings (USD) | Vinyl Savings (USD) | Difference (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold (Zone 6-8) | 1500 | 750 | 750 |
| Moderate (Zone 4-5) | 1000 | 500 | 500 |
| Hot (Zone 1-3) | 500 | 250 | 250 |
Aesthetic Considerations and Customization Options

Source: trulogsiding.com
Choosing between steel and vinyl siding involves more than just durability and cost; aesthetics play a crucial role in enhancing your home’s curb appeal and overall value. The right siding can dramatically transform the look of your house, reflecting your style and potentially increasing your property’s worth. Let’s explore the aesthetic differences and customization options available for both materials.
Steel siding offers a wide array of colors and styles, mimicking the look of wood, brick, or stone. While traditionally associated with more industrial or modern designs, advancements in manufacturing allow for more diverse aesthetic options. Vinyl siding, on the other hand, has historically been known for its classic and more traditional appearance, but modern vinyl siding comes in an incredibly wide range of colors and textures, often mimicking the appearance of wood shake or even more contemporary materials.
Steel Siding Aesthetics and Customization
Steel siding boasts impressive durability and color retention, meaning the color is less likely to fade over time compared to vinyl. The surface can be textured to imitate wood grain, stucco, or even a smooth, contemporary finish. Color options are extensive, ranging from classic earth tones to bold, modern shades. Customization is primarily achieved through color selection and the choice of panel profiles (e.g., horizontal, vertical, or even scalloped). For instance, a homeowner might choose a deep charcoal grey steel siding with a wood-grain texture to create a sophisticated, modern farmhouse aesthetic. Conversely, a sleek, smooth, white steel siding could give a home a clean, contemporary feel.
Vinyl Siding Aesthetics and Customization
Vinyl siding offers a vast palette of colors, often exceeding the options available in steel. While the color may fade slightly over time with prolonged sun exposure, the range of textures and styles is substantial. Many manufacturers offer profiles mimicking wood shakes, clapboard, or even stone. Customization extends beyond color and texture to include accessories like trim pieces, window surrounds, and corner boards, allowing for a high degree of design flexibility. For example, a homeowner might opt for a light beige vinyl siding with a subtle wood grain texture to create a classic, welcoming feel. Or, they might choose a bolder color like deep red or navy blue with a smooth finish for a more modern look. The addition of decorative trim can further enhance the aesthetic appeal.
Impact on Curb Appeal and Property Value
The choice of siding significantly impacts a home’s curb appeal and, consequently, its market value. A well-maintained, aesthetically pleasing exterior can attract potential buyers and command a higher price. For example, a home with outdated, faded vinyl siding might sell for less than a similar home with newer, high-quality steel or vinyl siding in a stylish color and profile. Conversely, a home with updated, attractive siding can increase its perceived value, potentially leading to a quicker sale and a higher profit for the seller. The choice should reflect the overall architectural style of the house and the neighborhood. A modern, sleek design might be more appropriate for a contemporary home in a new development, while a more traditional look might be better suited for a historic home in an established neighborhood.
Aesthetic Feature Comparison
| Feature | Steel Siding | Vinyl Siding |
|---|---|---|
| Color Durability | Excellent; resists fading | Good; may fade slightly over time |
| Texture Options | Wide variety; wood grain, stucco, smooth | Extensive; wood shake, clapboard, smooth |
| Ease of Cleaning | Easy; typically requires only occasional rinsing | Easy; typically requires only occasional rinsing |
| Style Options | Modern, contemporary, rustic | Traditional, modern, farmhouse |
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Choosing between steel and vinyl siding involves considering not just upfront costs and aesthetics, but also the long-term environmental consequences. Both materials have impacts throughout their lifecycles, from manufacturing and transportation to eventual disposal. Understanding these impacts can help homeowners make informed decisions aligned with their sustainability goals.
Manufacturing steel siding is energy-intensive, requiring significant amounts of iron ore and coal, leading to greenhouse gas emissions. Vinyl siding, primarily made from petroleum, also contributes to carbon emissions during its production. Transportation of both materials adds to their carbon footprint, especially over long distances. Disposal presents another challenge; steel can be recycled, but vinyl often ends up in landfills, where it persists for centuries.
Manufacturing Processes and Emissions
Steel siding production involves a complex process of mining, smelting, and rolling. These steps generate considerable air and water pollution, including greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and particulate matter. The energy needed for these processes often relies on fossil fuels. Vinyl siding manufacturing, while less energy-intensive than steel in some aspects, utilizes petroleum-based raw materials, contributing to reliance on non-renewable resources and emitting greenhouse gases. The manufacturing process of vinyl also releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere.
Recyclability and End-of-Life Management
Steel siding possesses a significant advantage in recyclability. Steel is a highly recyclable material, meaning it can be melted down and reused repeatedly without significant loss of quality. Many scrap metal recycling programs readily accept steel siding, diverting it from landfills and reducing the demand for newly mined iron ore. In contrast, vinyl siding is less easily recycled. While some recycling programs exist, they are not as widespread, and the process often results in downcycling—converting the vinyl into lower-quality products. Much vinyl siding ends up in landfills, contributing to plastic waste accumulation and environmental pollution. For example, a large-scale demolition project might generate tons of vinyl siding, placing a strain on landfill capacity and potentially leading to leaching of harmful chemicals into the soil and groundwater.
Environmental Considerations: A Comparison
- Steel Siding:
- Advantages: High recyclability, durable and long-lasting, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Disadvantages: Energy-intensive manufacturing process, potential for air and water pollution during production and transportation.
- Vinyl Siding:
- Advantages: Lower manufacturing energy compared to steel in some stages, relatively low maintenance.
- Disadvantages: Made from non-renewable resources (petroleum), low recyclability rate, significant landfill contribution, potential for release of harmful chemicals during production and disposal.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, the “best” siding choice—steel or vinyl—depends entirely on your priorities and circumstances. While vinyl often presents a lower upfront cost, steel boasts superior longevity and durability, potentially saving money in the long run through reduced maintenance and repairs. By carefully considering the initial investment, ongoing maintenance needs, energy efficiency implications, and aesthetic preferences, you can confidently choose the siding that best aligns with your budget and long-term goals for your home.
FAQ Explained: Cost Of Steel Siding Vs Vinyl
What about insurance implications? Does one type of siding affect home insurance premiums?
Yes, some insurance companies might offer slight discounts for homes with fire-resistant materials like steel siding. However, this varies widely by insurer and location, so it’s best to check with your provider.
How long does the installation process typically take for each type of siding?
Installation time depends on house size and complexity, but generally, vinyl siding installation is faster than steel. Expect a few days to a couple of weeks for a typical-sized house.
Can I install the siding myself, or is professional installation always necessary?
While DIY is possible for vinyl, it’s generally recommended to hire professionals for both steel and vinyl to ensure proper installation and avoid warranty issues. Steel siding is especially challenging for DIYers.
Are there financing options available for siding replacement projects?
Many home improvement companies offer financing plans, and some credit cards provide options for large purchases. Check with your contractor and bank for available options.
What’s the typical lifespan of steel and vinyl siding?
Steel siding can last 50 years or more with proper care. Vinyl siding typically lasts 20-30 years, but its lifespan can be shorter depending on climate and maintenance.
Comments are closed.